Texas Instruments Question Bank continued from Part 1
Q. Draw 2:1 Mux using pass transistors.
Ans: Two pass transistors are required to design 2:1 Mux.
Q. Draw 2:1 Mux using transmission gates.
Ans: Two transmission gates are required to design 2:1 Mux.
Q. What is setup and hold time?
Ans: Setup time is the minimum amount of time that an input signal (to the device) must be stable before the active edge of the clock arrives in order to avoid possible metastability.
Hold time is the minimum amount of time that an input signal (to a sequential device) must be stable after the active edge of the clock arrives in order to avoid possible metastability.
(In metastable state, the circuit may be unable to settle into a stable state ‘0’ or ‘1’ logic level within the time required for the proper circuit operation).
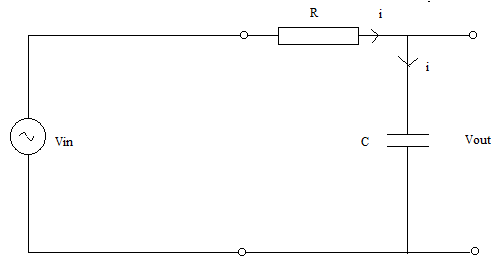
Q. What is the time constant of an ideal integrator? Draw its circuit diagram.
Ans: The time constant of an ideal integrator is defined by the product of the capacitance and resistor used.
τ=RC
where,
τ= time constant
R=Resistor
C=capacitor
The circuit diagram of integrator is shown:
Q. What are the different types of capacitors? What does X7R and X5R in MLCC (multilayer ceramic capacitor) mean?
Ans: The different types of capacitors are named after the type of dielectric used in capacitor. Few names are mentioned below:
- Ceramic capacitor: are also known as Disc capacitors and are made by coating two sides of a small porcelain or ceramic disc with silver. These are then stacked together to make ceramic capacitor. These have high dielectric constant.
- Electrolytic capacitor: The foil plates are anodized with a DC current. Some electrolytic capacitors are Aluminium Electrolytic capacitor, Tantalum Electrolytic capacitor, etc.
- Film capacitor: These capacitors are most common capacitors with difference in their dielectric properties. These include polyster, Teflon,polycarbonate, etc.
- Variable capacitor: These type of capacitors can vary the capacitance by changing the distance between plates or effective area of capacitor.
- Silver mica capacitor: These are made from depositing a thin layer of silver on a mica dielectric and are stable with respect to time.
X5R is described here:
X=minimum temperature range -55o C
5=maximum temperature range +85 o C
R= percentage of capacitance change permitted +/-15%
Similarly, for X7R:
X=minimum temperature range -55o C
7=maximum temperature range +125 o C
R= percentage of capacitance change permitted +/-15%
Q. What is the process involved in calling a mobile?
Ans: Mobile is an electronic device which gives full duplex communication and use wireless technology. First of all it needs to establish connection to the available service providers network. It scans the group of forward control channels and gets connect to the strongest one. This keeps on happening till the mobile is switched on. Now when a call is made through the device, a request is initiated on the reverse control channel. Along with the request, MIN (Mobile Identification Number), ESN (Electronic Serial Number) and the dialled phone number also get transferred. When base station receives this data it sends the data to MSC (Mobile Switching Center). The request then gets validated by MSC by checking MIN with the database records. If it is valid PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) make a connection. Then MSC requests base station to move the phone to a voice channel so that the conversation can continue. Now when you speak through the cellphone, the voice in its electrical signal form is converted into strings of numbers. The microphone of the phone converts the sound of your voice to a pattern of electrical signal. The numbers are packed up in radio wave and are transferred through the antenna of mobile. These information travels with the speed of light and reach to the nearest cell phone mast. The mast on receiving the signals passes them to base station. From the base station the calls are routed to their destination.
You may love to read Interview Experience – WIPRO Limited – Telecom Domain
Q. How voice gets modulated?
Ans: The process of imposing speech information with another wave called an input signal (career wave) is known as modulation. In other words the modulation changes the shape of carrier wave to encode the data contained in it. A wave can get modulated in three domains:
- amplitude
- frequency
- phase
Q. What are different OSI Layers?
Ans: https://www.vlsifacts.com/ericsson-india-technical-interview-question-bank-part-1/
Q. Explain the difference between slotted aloha and time division multiplexing.
Ans: Slotted aloha is a refinement of pure aloha to increase the efficiency of pure aloha. In slotted aloha the time is divided into fixed length of time slots and the station is allowed to send data only at the beginning of the time slot. If it misses this moment then it must wait until the beginning of the next time slot. Thus the possibility of collision of packets decreases.
TDM (Time division multiplexing) is a method of transmitting multiple data through a single signal separated into segments of short duration. In other words, the data streams have predefined slot positions in the combined stream. And the transmitter and receiver must be synchronized so that receiver can be aware of which slots belong to which input stream.
Q. What is difference between broadcast domain and collision domain?
Ans: Broadcast is a type of communication where a device sends a single copy of data and that copy is delivered to each and every device in the network. As the number of devices in the network increase, the quality decreases due to the smaller bandwidth dedicated to each device in the network and also due to decreasing processing power of computers/devices.
In collision domain, collision can occur between the packets. When two devices send data packet at the same time collision may occur and the data packet will need to be transmitted again by both the sender devices. Thus efficiency of the network is decreased. Collision often occurs in hub as each port in hub is in same collision domain while each port on bridge, router or switch is in separate domain.