Aricent Technologies Technical Interviews Question Bank continued from Part 3
Q-16. What is half-duplex channel? Give a real-life application of it.
A : Half-duplex channel is a medium of communication in which the sender and receiver are capable of transmitting or receiving but not both at the same time for example, a walkie-talkie.
Q-17. What is full-duplex channel? Give an example.
A : Full-duplex channel is a medium of communication in which the sender and receiver are capable of transmitting or receiving and both can transmit/receive at the same time for example, a telephone.
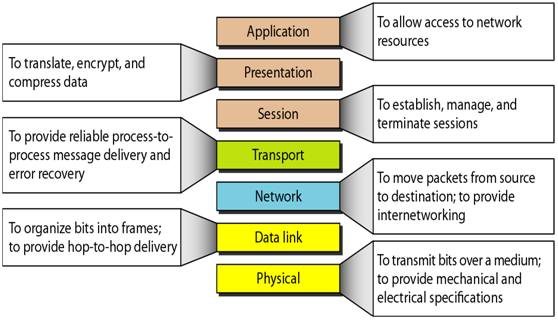
Q-18. What is OSI? Explain the OSI layers in order.
A : OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection. For data communication, the ISO (International Standard Organization) has given a layered framework for understanding and designing purpose,nk called as OSI. The overall task is subdivided in multiple levels, each called a Layer. The entire process of data transmission is broken down to network functions. The network functions are grouped as per their characteristics & each group of functions is called a layer. All the OSI layers can be briefly described as follows –
Q-19. At which OSI layer does the retransmission of packets take place?
A : The retransmission of packets takes place in the Network layer of OSI model.
Q-20. Explain TCP/IP. Give their real-life applications.
A : TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol and is a basic, connection-oriented and reliable transport protocol of the Internet. TCP offers full-duplex service in which data can flow in both directions at the same time. It adds reliability and connection-oriented features to the services of IP. It is a three-phase service which implies that two TCPs establish a dedicated connection between themselves in the first, transfer data in the second and then release the path in the third phase. It can be used for secure online payment transactions as it uses Acknowledgement (ACK) mechanism to check the safe arrival of data.
Gautam Vashisht, JIIT Noida
Continued to Part 5