The chip design includes different types of processing steps to finish the entire flow. For each and every step, the design process requires a dedicated EDA tool. These tools have the flexibility to import or export different types of files.
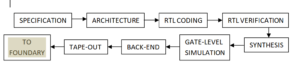
The picture below shows the various steps of the design flow:
Here is a brief description of each step:
- SPECIFICATION: This is the crucial step as it will decide the future of the product. Lots of activity goes on to gather the market requirement. One may take feedback from potential customers on what they are looking for or what the expectations are. Once this done, the specification sheet along with finer technical details are shared to next team.
- ARCHITECTURE: Now this is the step where main work starts. With the help of specification, design engineers decide the architecture and a layout is created for the IC using EDA tools.
- RTL CODING: RTL is an acronym for register transfer level. This is where the detailed system specifications is converted into VHDL or Verilog language (Hardware Description Language) showing how data is transferred from register to register. This also goes through functional verification process in next step.
- RTL VERIFICATION: Register Transfer level is one of the important step which ensures that the design is logically correct without major timing errors. It is very advantageous to perform this step at early stage. A testbench file may be used to verify the design using EDA tools.
- SYNTHESIS: In this process RTL is transferred to netlist (gate level netlist). This is done with the help of FPGA/CPLD/ASIC hardware tools. These target boards may be accessed using IDE’s provided by different vendors.
- GATE-LEVEL SIMULATION: The verification of gate level simulation of the logic generated is very important. In this step various kinds of checks are included like: functionality check, timing check and physical analysis check.
- BACK-END: Here the final design after synthesis is given to the IC manufacturer.
- TAPE-OUT: It is the process under back-end only where the final result of FRONT-END is provided to the manufacturer in form of photomask. Then the manufacturer performs wafer processing, packaging, testing, and delivery of samples to test the physical IC.
- TO FOUNDRY: once the samples are tested and verified, then the design is sent for mass production.
1 comment for “VLSI Design Flow”